Less than a year after a global law enforcement takedown severely disrupted its operations, LummaStealer has not only survived, but it’s thriving again.
Bitdefender researchers report a sharp resurgence in the infostealer’s activity, now fueled by a stealthy delivery chain centered on CastleLoader, a modular script-based loader designed to evade traditional security controls.
LummaStealer is an infostealer for Windows systems that extracts browser-stored credentials and cookies, 2FA tokens and authentication extensions, cryptocurrency wallets (MetaMask, Electrum, Exodus), password manager data (KeePass), remote access tools (AnyDesk), documents, clipboard contents, and Discord, Steam, VPN, FTP, and email client data.
Its goal is to facilitate account takeovers, identity theft, financial fraud, and extortion. In some cases, stolen private data or adult-themed lures are repurposed for coercive tactics like blackmail.
The analysis reveals that LummaStealer’s developers rapidly rebuilt their infrastructure and adjusted their tactics following Microsoft’s May 2025 operation that disabled over 2,300 of the malware’s command-and-control (C2) domains. Bitdefender’s latest telemetry shows Lumma’s campaigns are once again spreading globally, exploiting social engineering rather than software vulnerabilities to gain access to systems.
LummaStealer, first seen in late 2022, operates under a malware-as-a-service (MaaS) model, allowing affiliates to deploy the stealer through a rented infrastructure. Its developers offer a tiered subscription system that gives clients access to C2 management panels, payload customization, and a wide range of stealing capabilities. Despite the international takedown effort led by Microsoft, the malware’s operators quickly migrated to bulletproof hosting and resumed activity.
Central to this resurgence is CastleLoader, a heavily obfuscated loader that executes payloads entirely in memory and communicates with C2 servers via stealthy channels. The Bitdefender team found overlapping infrastructure between CastleLoader and LummaStealer, suggesting collaboration or shared service providers within the cybercrime ecosystem.
CastleLoader enabling Lumma’s comeback
CastleLoader acts as a delivery framework for LummaStealer, evading detection with sandbox-awareness, in-memory payload execution, and environmental persistence. In the latest campaigns, CastleLoader is often compiled as AutoIt executables, with the embedded scripts obfuscated using dictionary-based variable renaming, junk code insertion, and multi-stage decryption routines.
One identifiable characteristic is the loader’s use of anomalous DNS requests, deliberate failed lookups for randomly generated domains. These serve as a weak form of sandbox detection but leave behind a detectable network signature that defenders can monitor.
Once past environmental checks, the loader creates persistence via scheduled tasks or startup shortcuts, often storing its files under misleading directories such as \CraftStitch Studios Inc. Ultimately, CastleLoader decrypts and launches LummaStealer, either embedded or fetched from a C2 server.
Varying distribution and infection chains
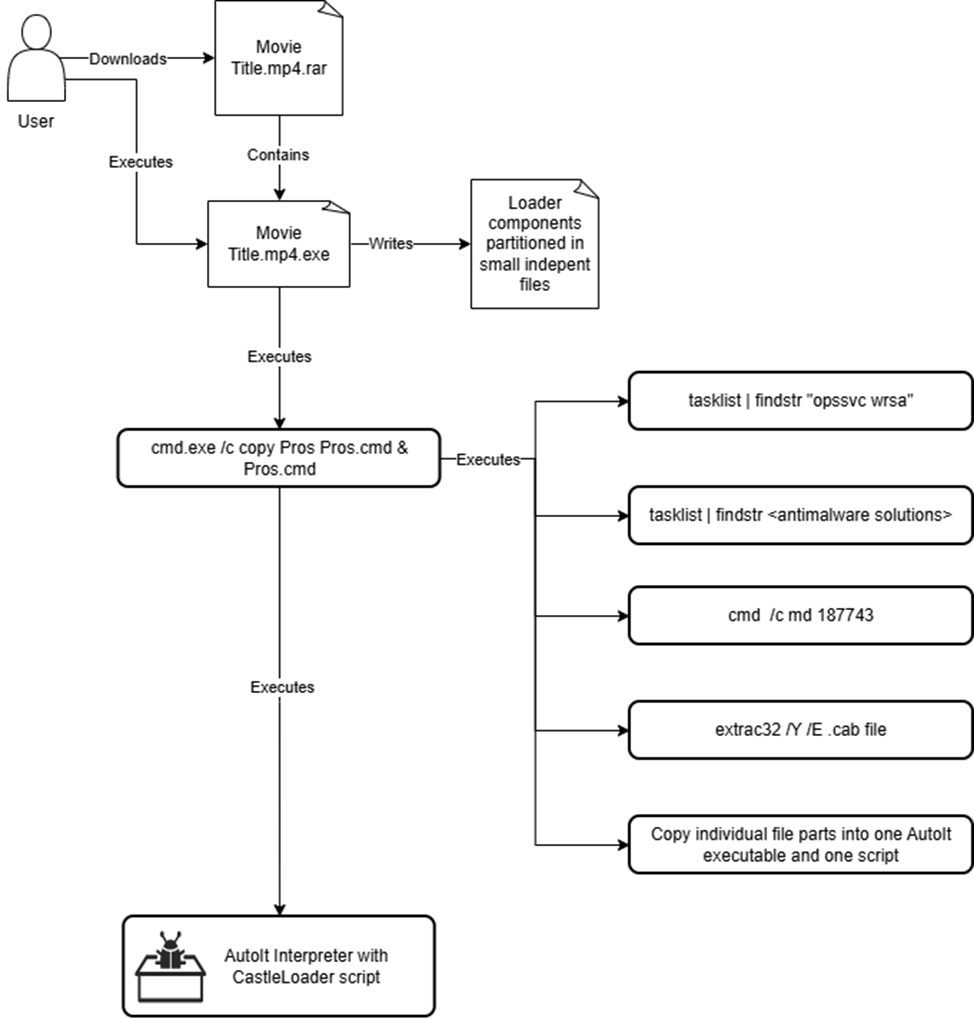
Lumma’s new wave of campaigns leans heavily on social engineering to infect users, with no reliance on software vulnerabilities. CastleLoader’s infection chains often begin with fake installers disguised as cracked games, pirated software, or newly released movies. In these cases, users willingly execute the malware, believing it to be legitimate content.
Bitdefender
Prominent delivery vectors include:
- ClickFix fake CAPTCHA pages that instruct users to execute clipboard-injected PowerShell commands
- Bait downloads from platforms like Steam Workshop, Discord, or torrent sites
- Double extension files (e.g., .mp4.exe) to trick users into executing malicious content
- Obfuscated VBA scripts, sometimes wrapped in scheduled tasks for persistence
- Once executed, the CastleLoader payload proceeds with installation, persistence setup, and payload decryption, ultimately delivering LummaStealer to the infected system.
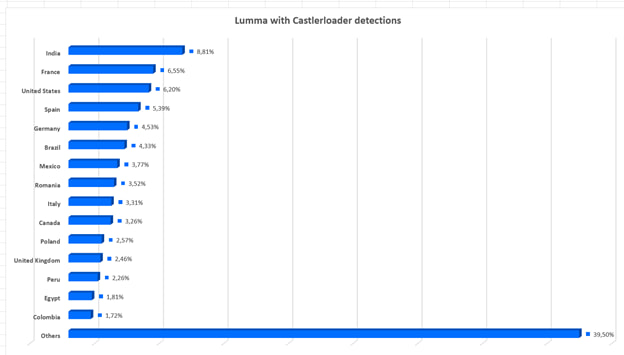
Bitdefender’s telemetry shows that LummaStealer infections are active in India, the United States, and Europe, with distribution patterns shifting depending on affiliate targets.
Users are advised to avoid downloading cracked software, pirated media, or adult content from unofficial sources, and never execute clipboard content or PowerShell commands from websites.
If you liked this article, be sure to follow us on X/Twitter and also LinkedIn for more exclusive content.


